What's scarier than a haunted house or a creepy clown? For millions worldwide, it's phobias - an intense, irrational fear of specific objects, situations, or activities. According to the American Psychiatric Association, phobias are a type of anxiety disorder that can cause individuals to go to great lengths to avoid the source of their fear, even if it's harmless.
Around 9% of US adults have a specific phobia. Despite how common phobias are, only about one-third of people seek phobia treatment. This is largely because there are many misconceptions about phobias out there. It’s hard to seek treatment for something you don’t know is a problem, so let’s dive into what a phobia is and how phobia treatment works.
What is A Phobia?
When we think of phobias, we often think of common fears like heights, spiders, or enclosed spaces. While these are common phobias, they are far from the only ones. Phobias can range from general fears of abstract concepts to very specific situations.
At their core, phobias are a type of anxiety disorder characterized by an excessive, irrational fear of a particular object or situation.
What is the difference between fear and phobias?
While fear is a normal response to a perceived threat, phobias go beyond the typical range of apprehension. They can cause individuals to experience intense physical and emotional symptoms, such as sweating, rapid heartbeat, trembling, and a sense of impending doom. In severe cases, phobias can even lead to panic attacks, which can be debilitating and interfere with daily life.
It's important to note that not all fears are phobias. While fears are a natural part of life, phobias are intense and persistent, lasting for six months or more. They also tend to cause significant distress and impairment in social, occupational, or other areas of functioning. In other words, phobias can seriously impact a person's quality of life and prevent them from doing things they enjoy or need to do.
The 3 Main Types Of Phobias
The American Psychiatric Association recognizes three main types of phobias: specific, social, and agoraphobia.
Agoraphobia and social phobia (social anxiety) are often considered their own disorders, while there are numerous types of specific phobias, some of which we’ll explore below.

Social Phobias
Also known as social anxiety disorder, social phobias are an intense fear of social situations, such as public speaking, meeting new people, or eating in front of others. People with social phobia may avoid or endure social situations with intense fear and anxiety.
Social phobia often develops in adolescence or early adulthood and can be caused by genetics, brain chemistry, or learned behavior.
Specific Phobias
This is the most common type of phobia widely diagnosed among individuals. They are intense fear or anxiety of a specific object or situation, such as flying, spiders, heights, or needles. People with specific phobias may go to great lengths to avoid the feared object or situation, and their fear may be so severe that it interferes with their daily life.
These phobias usually develop in childhood or adolescence and can be triggered by a traumatic event or learned behavior.
Agoraphobia
This type of phobia is the fear of being in situations or places where escape may be difficult or embarrassing, such as crowded places, public transportation, or open spaces. People with agoraphobia may avoid these situations altogether or require a companion.
Agoraphobia can develop after experiencing a panic attack or a traumatic event, or it may be a complication of another anxiety disorder.
Symptoms of Phobias

Phobias can develop at any age and can be triggered by various things. You may be struggling with a phobia if you experience:
Intense fear or anxiety
The primary symptom of a phobia is intense fear or anxiety when exposed to the object or situation that triggers the phobia. This fear or anxiety can be overwhelming and make the person feel like they are in immediate danger, even if there is no real threat.
Avoidance behavior
As a result of intense fear or anxiety, people with phobias often engage in avoidance behavior. They will go to great lengths to avoid the object or situation that triggers their phobia, even if it disrupts their daily lives. For example, someone with a phobia of flying may refuse to travel by plane, even if it means missing out on important events or opportunities.
Physical symptoms
Phobias can also cause a range of physical symptoms, including:
- Rapid heartbeat
- Sweating
- Trembling or shaking
- Shortness of breath or difficulty breathing
- Nausea or dizziness
- Chest pain or tightness
- Chills or hot flashes
These physical symptoms are the body's natural response to the perceived threat of the phobia. They are part of the "fight or flight" response designed to prepare the body to respond to danger.
Cognitive symptoms
Phobias can also cause cognitive symptoms, such as:
- Obsessive thinking about the object or situation that triggers the phobia
- Persistent worry or anxiety about encountering the object or situation
- Difficulty concentrating or focusing on tasks
- Irrational beliefs or thoughts about the object or situation
These cognitive symptoms can be just as distressing as physical symptoms and can interfere with a person's ability to function in their daily life.
Phobias and Panic Attacks
Exposure to the object or situation that triggers the phobia can sometimes lead to a panic attack. Panic attacks are intense and overwhelming feelings of fear or anxiety, including physical symptoms such as rapid heartbeat, sweating, and shortness of breath. Panic attacks can be frightening and reinforce the phobia by making the person even more afraid of the object or situation that triggers the attack.
Causes of Phobias
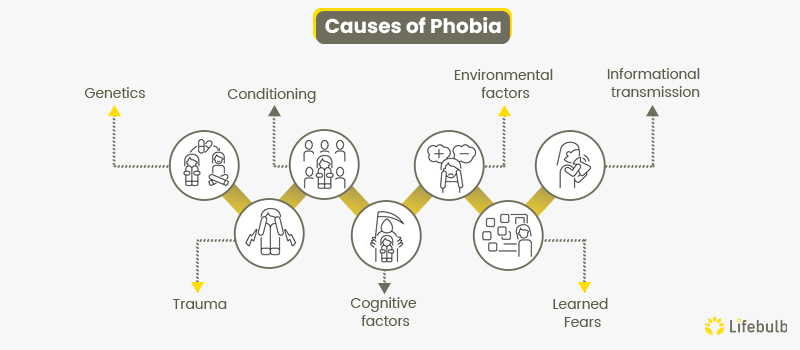
Phobias are caused by many different factors, including;
- Genetics: Phobias may have a genetic component, as they run in families. Some studies have identified specific genes associated with increased anxiety disorders and phobias risk. However, the specific genetic factors involved in phobias are not fully understood.
- Trauma: A traumatic event can trigger the development of a phobia. For example, a person who experiences a car accident may develop a phobia of driving or being a passenger in a car. This type of phobia is known as a specific phobia. Trauma can also lead to the development of more general phobias, such as agoraphobia, which is a fear of being in public spaces.
- Conditioning: Phobias can be learned through classical conditioning, which involves associating a neutral stimulus with a negative experience. For instance, if a person experiences a panic attack while in an elevator, they may develop a phobia of elevators. Over time, the person may associate elevators with fear, and the phobia may become more pronounced.
- Cognitive factors: How a person thinks about a situation or object can also contribute to developing a phobia. A person who tends to catastrophize or overestimate the danger of a situation may be more likely to develop a phobia. In addition, negative self-talk, such as telling oneself that a situation is dangerous or impossible to handle, can contribute to the development of phobias.
- Environmental factors: Environmental factors, such as upbringing and life experiences, can also contribute to developing a phobia. For example, a person raised in a highly sheltered environment may be more likely to develop a phobia due to a lack of exposure to different stimuli. Conversely, someone who has experienced trauma or a stressful life event may be more vulnerable to developing a phobia.
- Informational transmission: Informational transmission refers to the process by which fears and phobias are transmitted from one person to another through social learning. A kid who observes a parent expressing fear or avoidance of a specific situation may be more likely to develop a phobia of that situation themselves. Also, cultural attitudes and beliefs about particular objects or situations can contribute to phobias development.
Understanding these underlying symptoms & causes of phobias can help with their prevention, diagnosis, and treatment. If any of the above symptoms or causes ring a bell to you or sound familiar, then it is high time you find a therapist nearby and book a session right away.
The 5 Subtypes of Specific Phobias
There are 5 subtypes of specific phobias, although the actual list within these subtypes is impossible to count. The subtypes are: Animal type (fear of dogs, spiders, birds, etc.), natural environment type (storms, heights, darkness, water, etc.), Blood injection or injury (blood, medical procedures, vomit, etc.), Situational type (flying, driving, being in an elevator, etc.), and others.
Common Types of Phobias
Some of the most common types of phobias include:
- Fear of Heights (Acrophobia)
Acrophobia, the fear of heights, transcends a simple aversion to tall structures. It involves an intense and irrational fear that can lead to avoidance of elevated spaces, impacting one's ability to engage in activities like climbing stairs or enjoying scenic views.
- Fear of Spiders (Arachnophobia)
Arachnophobia, the fear of spiders, is a widespread phobia that triggers intense anxiety at the sight of these eight-legged creatures. From harmless house spiders to exotic species, arachnophobia can lead to extreme reactions, ranging from mild discomfort to panic attacks.
- Fear of Flying (Aviophobia)
Aviophobia, or the fear of flying, extends beyond mere nervousness during air travel. This phobia can result in debilitating anxiety, potentially limiting individuals from experiencing the vast opportunities that air travel affords.
- Fear of Public Speaking (Glossophobia)
Glossophobia, the fear of public speaking, goes beyond typical nervousness. This intense fear can hinder personal and professional growth, impacting individuals in academic, professional, and social settings.
- Fear of Enclosed Spaces (Claustrophobia)
Claustrophobia, the fear of enclosed spaces, can trigger panic attacks in situations like elevators or crowded rooms. Understanding this phobia is essential, as it influences personal choices and the ability to navigate various environments.
- Fear of Snakes (Ophidiophobia)
Ophidiophobia, the fear of snakes, taps into deep-seated fears ingrained in human evolution. Whether encountering snakes in the wild or even viewing images, individuals with this phobia experience heightened anxiety and avoidance behaviors.
- Fear of the Dark (Nyctophobia)
Nyctophobia, the fear of the dark, can persist beyond childhood. This phobia influences nightly routines, impacting sleep quality and overall well-being. Understanding the roots of nyctophobia is crucial for effective management.
- Fear of Needles (Trypanophobia)
Trypanophobia, the fear of needles, extends beyond discomfort. This phobia can lead to avoidance of necessary medical procedures, impacting healthcare decisions and potentially compromising overall health.
- Fear of Failure (Atychiphobia)
Atychiphobia, the fear of failure, goes beyond a natural aversion to setbacks. This intense fear can hinder personal and professional growth, leading to avoidance of challenges and opportunities.
- Fear of Dogs (Cynophobia)
Cynophobia is the fear of canines and dogs. The fear goes beyond general discomfort or dislike of these creatures. People with Cynophobia may go to great lengths to avoid seeing or being near a dog, including only leaving the house at certain times or going a different route if a known dog is out. Seeing a dog or being approached by one causes extreme anxiety and possibly panic attacks.
Treatment Options for Phobias

There are effective treatment options available that can help individuals overcome their fears and regain control. This article will explore some of the most common and successful treatments for anxiety or phobia.
Therapy For Phobias
One of the main treatment options for phobia is Therapy. Psychotherapy or talk therapy can provide individuals with the tools and techniques to effectively develop coping skills and strategies to overcome their fear of particular objects or situations. The different types of techniques used to treat phobias include:
- Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy
- Interpersonal Therapy
- Cognitive Restructuring
- Systematic Desensitization
- Mindfulness-based therapy
Treatment for phobias will largely depend on the individual’s type of phobia, severity of phobia, and any comorbid conditions (like anxiety or depression).
Exposure Therapy and Desensitization
Exposure therapy is one of the most common and effective forms of treating phobias. In fact, people see between 80% to 90% recovery rate when exposure therapy is used.
In this therapeutic approach, the therapist exposes individuals to their feared object or situation gradually and controlled. By repeatedly experiencing the fear-inducing trigger, individuals learn that their fear is unfounded and the trigger is actually safe. The ultimate goal is to desensitize individuals to the phobic stimulus, enabling them to face their fears with reduced anxiety.
There are three different approaches to exposure therapy
- Systematic Desensitization: A gradual and systematic approach to facing fears, systematic desensitization involves exposing individuals to feared stimuli in a controlled manner. This process, often guided by a therapist, allows for the incremental reduction of anxiety associated with phobias.
- Virtual Reality Exposure Therapy: Leveraging advanced technology, virtual reality exposure therapy immerses individuals in simulated environments related to their phobias. This innovative approach provides a safe yet realistic platform for gradual exposure, enhancing the effectiveness of desensitization.
- Flooding Technique: In contrast to systematic desensitization, flooding involves immediate and prolonged exposure to the feared stimulus. While intense, this approach aims to extinguish the conditioned fear response through prolonged exposure, facilitating a more rapid form of desensitization.
In navigating the path to recovery from phobias, the array of therapeutic approaches, coupled with exposure therapy, desensitization techniques, and medication options, provides individuals with a multifaceted toolkit for managing and overcoming their fears. Seeking professional help is not just a choice; it's a transformative journey toward reclaiming a life unburdened by the chains of irrational anxieties.
Debunk a few myths over phobias.
Phobias are often misunderstood and surrounded by myths that prevent individuals from seeking the help they need. Here, we will debunk some common misconceptions about phobias and shed light on the reality of these anxiety disorders. By understanding the truth, we hope to encourage people to overcome their hesitations and understand what to expect during treatment for phobias.
Myth 1: People with phobias are mentally unstable.
Fact: Phobias are severe psychiatric conditions. They are not a sign of being crazy or mentally unstable. Phobias are real and distressing to those experiencing them. It is essential to eliminate judgment and stigma surrounding phobias to create a supportive environment for seeking help.
Myth 2: Phobias are not that serious.
Fact: Phobias are highly distressing and can significantly impair a person's daily functioning. They can lead to avoidance of certain situations, persistent anxiety, panic attacks, and other psychiatric conditions.
Myth 3: Phobias are just exaggerated fears.
Fact: Phobias are not overrated fears, but an extreme biological and psychological fear response characterizes them. The brain and body react disproportionately to the feared object or situation, leading to heightened anxiety and physical symptoms.
Myth 4: Phobias can always be rational.
Fact: By definition, a phobia is an irrational fear. While fear is a rational response to a real threat, phobias involve an exaggerated fear response to situations or objects that do not pose a genuine danger. Acknowledging the irrational nature of phobias helps to understand the unique challenges faced by individuals with specific phobias.
Myth 5: Phobias can never be overcome.
Fact: Phobias can be overcome effectively with the right treatments. While phobias can be chronic if left untreated, seeking appropriate therapy can lead to significant improvement. Cognitive-behavioral therapy, exposure therapy, and other behavioral and cognitive strategies have proven to be successful in helping individuals conquer their fears.
Why Do People Hesitate to Seek Treatment For Phobias
Despite the availability of effective treatments, some individuals still hesitate to seek help for their phobias. The reason behind this hesitation is:
- Lack of Awareness: Many people may not be aware that the extreme fear they are enduring is called phobia, which needs to be treated to overcome the symptoms. Also, if they know about them having phobias, then most of them aren't aware of the available treatment options or the success rates of therapy for them.
- Stigma and Judgment: The fear of being judged or stigmatized can prevent individuals from seeking therapy. Creating a safe and supportive environment where seeking help is encouraged and applauded is essential.
- Underestimating the Severity: Some individuals may downplay the impact of their phobias, believing that they are not severe enough to warrant treatment. Raising awareness about the potential consequences of untreated phobias can help individuals realize the importance of seeking help.
Overall, educating oneself or someone you know who has phobias is essential to overcome the potential consequence it can have on one's life and relationship. With the help of a mental health therapist, you or someone you know can overcome phobias and get over the extreme anxiety symptoms it can cause in one's life.
Conclusion
Understanding what is a phobia, why it occurs, and how to overcome it is essential for those seeking relief from the grips of fear. A phobia is not simply an exaggerated fear or a sign of weakness; it is a valid anxiety disorder that can significantly impact one's life. Phobias may stem from various causes, including genetics, learned fear, and traumatic experiences. However, the good news is that phobias are treatable conditions. Through therapy, individuals can regain control and find freedom from fear's shackles.
Leap, break free from fear's chains, and embark on a healing journey. At Lifebulb, our experienced therapists specialize in treating phobias using evidence-based approaches tailored to your needs. Contact us today, and let us guide you toward a future filled with courage, confidence, and newfound freedom.

